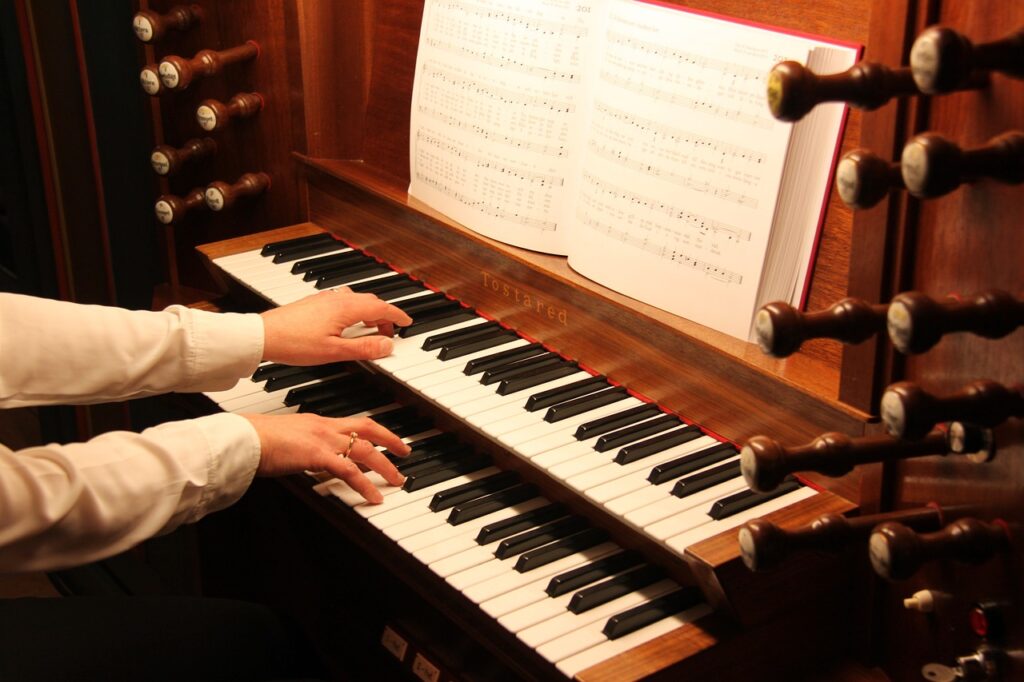
Church Organs in Silent Films: The Unsung Hero of Early Cinema
- By Josh Dove
Silent films may have lacked spoken dialogue but were never truly silent. Music played a crucial role in bringing these films to life, and one of the most dramatic and versatile instruments used was the church organ. From eerie horror films to grand epics, the church organ’s deep resonance heightened suspense, added grandeur, and evoked solemnity.
The Role of the Church Organ in Silent Films
Creating Emotion and Atmosphere
Before synchronized sound, filmmakers relied on music to convey emotion and enhance storytelling. The church organ, with its wide dynamic range and rich tones, could produce sounds that evoke suspense, drama, joy, or even fear. The organist had the power to shape the audience’s experience depending on a romantic scene or terrifying moment.
Live Accompaniment in Theaters
Unlike modern movie soundtracks, silent film scores were performed live in theaters. Many venues installed pipe or digital organs to provide powerful, immersive sound. Talented organists improvised music based on the film’s action, ensuring a unique performance each time. Some theaters even had resident organists who mastered the art of spontaneous composition.
The Church Organ’s Connection to Classic Silent Films
Horror and the Haunting Sound of the Organ
One of the most iconic uses of the church organ in silent films was in the horror genre. Movies like The Phantom of the Opera (1925), starring Lon Chaney, featured haunting organ music that intensified the film’s eerie atmosphere. The deep, resonant tones of the organ became synonymous with mystery, suspense, and the supernatural.
Grand Epics and Religious Themes
Silent films often explored religious and historical themes, making the church organ a fitting choice for their scores. Films like Ben-Hur: A Tale of the Christ (1925) and The King of Kings (1927) used the organ to create a sense of grandeur and reverence, reinforcing their spiritual narratives. The organ’s majestic sound helped audiences feel the weight of these dramatic stories.
The Legacy of the Church Organ in Film Music
Influence on Modern Film Scores
Even after the silent film era ended, the impact of church organs remained. The deep, resonant sounds of the organ continue to be used in modern film scores to evoke grandeur, mystery, or horror. Movies like Interstellar (2014) and The Exorcist (1973) utilize organ music to create unforgettable, spine-chilling moments.
Preservation of Silent Film Music
Today, silent film screenings with live organ accompaniment remain a cherished tradition. Film enthusiasts and musicians work to preserve this unique art form, performing original or reconstructed scores on historic theater organs. Organizations dedicated to silent cinema ensure that new generations can experience these films as they were meant to be seen—and heard.
Experience the Magic Yourself
Church organs played an important role in the silent film era, shaping the way audiences experienced cinema. The instrument’s versatility allowed organists to enhance films with emotion, tension, and grandeur. Though the era of silent films has passed, the church organ’s legacy endures, influencing modern soundtracks and keeping the magic of early cinema alive.
Explore our collection of digital organs designed to recreate the grandeur of classic cinema music. Contact us today to learn more.
Related Posts

Mondaino: Our Home

History of Church Organs

